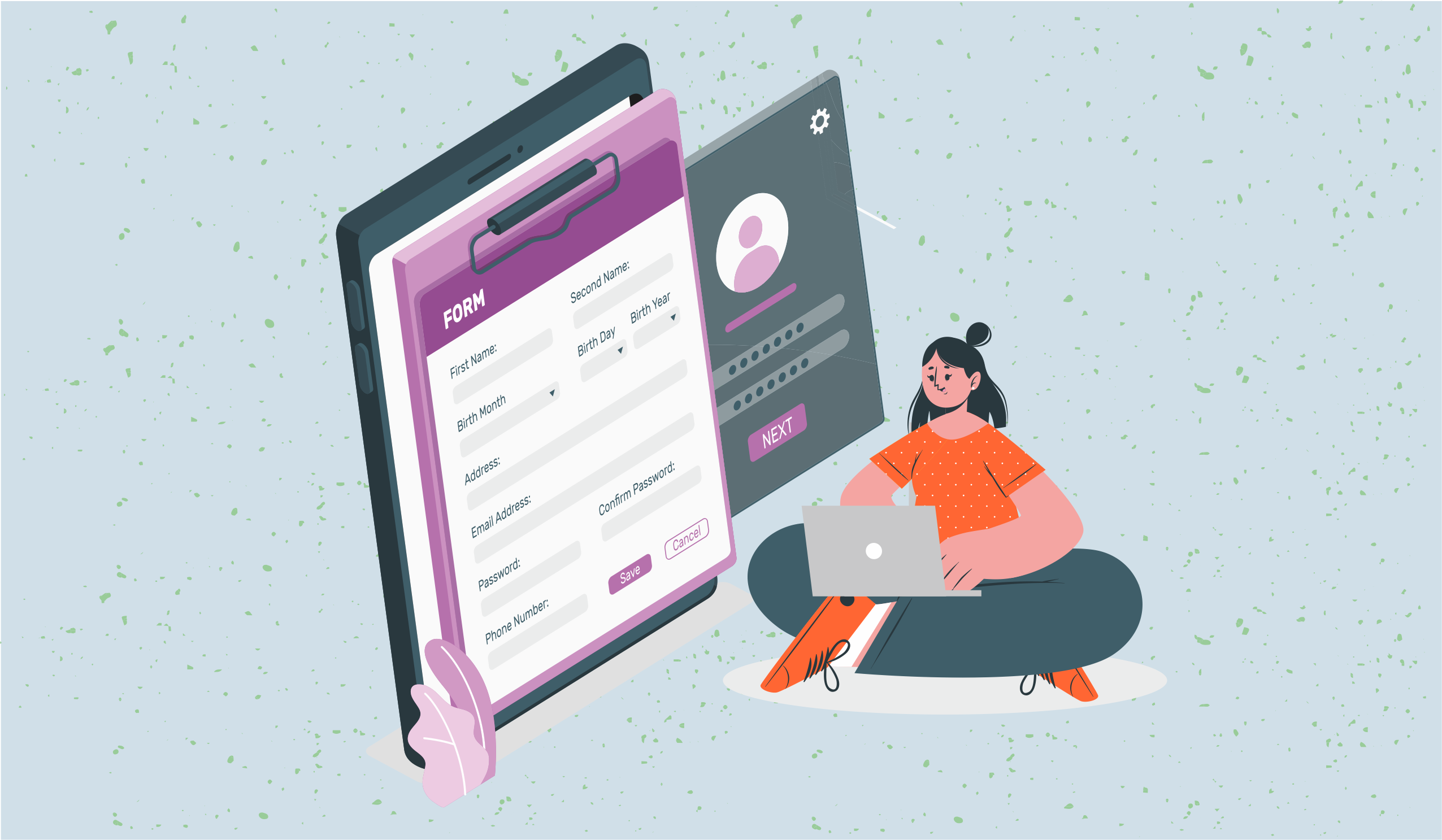
Mastering Excel for Effective Database Creation: Guide & Templates
Learn how you can create a database in excel in a step by step guide. Ends with free surprise database templates for you & your teams to use.

Introduction
Are you tired of struggling with complex database creation methods? Look no further – this step-by-step guide will empower you to become a master at using Excel for effective database creation. Whether you're a small business owner, a data analyst, or a student, mastering Excel is a valuable skill that can improve your productivity and efficiency. In this comprehensive guide, we will walk you through each stage of the database creation process, from understanding the basics of Excel to implementing advanced formulas and techniques. We will cover everything you need to know to create a well-organized and functional database that meets your specific needs.
Get your free Excel spreadsheet for business expenses [2024]
By the end of this guide, you will have the confidence and skills to tackle any database project using Excel, unleashing its full potential as a database management tool. Get ready to take your data management skills to the next level – let's dive in!
Any enterprise, big or small, deals with data to perform its day-to-day activities. As the business grows and develops, the data collected in the form of numbers also grows by the day. The ordeal of crunching numbers is a necessary, and even vital part of business, needed to glean useful information and insights about the financial status of the company. Usually, keeping track of accounts is left to a specialist - a bookkeeper or accountant, who could either be in-house or hired from an external firm.
For small businesses, outsourcing bookkeeping or hiring a qualified accountant may not be a viable option because of the cost, or the owner might just want to take care of the task themselves to reduce expenses. In that case, the business owner has one more task to add to the multitude of duties already on their plate - strategy, planning, client handling - and now bookkeeping. In the digital age, this no longer implies entering data manually in countless dusty ledgers, or doing calculations slowly one by one.
If you're using Excel only to import and export work, try Stackby! You can create custom no-code database in minutes with powerful views, unique data types, integrations and actionable dashboards.
Why Databases?
Data management is done on databases, and they aren’t necessarily used only by large corporations who handle tons of data about various products and clients. Small business owners can easily leverage databases to store, track, and control all kinds of data pertaining to their business. It's worth emphasizing that even trekking companies in the travel industry prioritize building the most effective data management strategy to boost destination sales, enabling them to suggest tours like the Tour du Mont Blanc based on their database insights.
Ideally, your database should enable you to retrieve and modify the information you’re looking for with just a few clicks. It should help you cross-reference, stay consistent, and keep your crucial business data safe and in one place.
Paying to use Database Management Systems provided by large vendors, either on the cloud or physically, might be expensive during the nascent stages of your business. But there are lightweight databases like Stackby that make your life easier while remaining light on the pockets. The most commonly used one, is of course, Microsoft Excel. It’s been around for 35 long years, and has helped millions of users store data, perform calculations on it, display it, and even programme it to their liking. But it’s a spreadsheet, not a database.
Why Excel?
The best part about Excel is its ease of use. A standard tool that’s even taught from the middle school level, basic knowledge of spreadsheets is an easy to acquire and highly useful skill in the long term. For a business owner, hiring an expert might be more convenient, but just equipping yourself with the basics is more than enough to take advantage of what Excel has to offer without getting too deep into its advanced features.
Top 12 Microsoft Excel Alternatives for Power-Packed productivity
As a business owner, you can analyze your data like sales numbers, future projections, expenses, and so on using Excel’s simple calculation features. The first step in all this is to create the database. Learning how to do that immediately puts you on the path to better data management. This article will explain how to do just that in a few simple steps.
Further for more advanced topics or troubleshooting explore excel help beyond this guide to unlock the full potential of Excel for your database needs.
Formatting and organizing data in excel for effective database creation
- Open up a new spreadsheet on Excel, and enter the title of your database in the first cell A1 on the top left.
- The spreadsheet is made up of rows and columns, and the first step is to enter the headers of the columns based on the data you want to collect.
- For example, your columns could display headers like “Product Name”, “Type”, “Units produced”, “Units sold”, and so on.
- Then you enter the headings for each row in the first column. Using the same example, the rows would be “Product 1”, “Product 2”, “Product 3” and so on.
- Use the keyboard shortcut ‘Tab’ to speed up the process and automatically jump to the next row as soon as you’re done with the previous one.
Importing & Adding data in Excel
- You can add data in two ways - either by manually inputting it, or importing it from existing files.
- To enter data manually, start typing the relevant info into the corresponding cells.
- Remember that rows are records - and must have data about only one single item. Any and all details about that item have to go into the same row.
- Columns function as fields, and the headers on top make sure that all the data in the rows follows the same sequence. If you enter the data in a column using a particular format or unit, keep it up throughout the table.
- To import data from an external source, go to the Data tab, where you have a set of options to import data - from text, HTML, a different database, etc.
- Select the right source, and ensure your data is formatted correctly so that it can be imported into Excel.
- Though this can be a tedious process, take it slow and stay cautious of making any errors in data entry, as they could cause trouble in the long term.
Convert your data into a table
- Now it’s time to create a data table in order to access the functions of a database.
- Select any cell with data entered in it and then go to the Insert tab > Table.
- Excel will automatically select all your data, but you should ensure there are no blank cells and deselect the cell with the data title in it.
- Check that all the selected cells are correct, and then proceed with the Ok button.
- To include any new data you enter, go to the small triangle on the bottom right of the table and drag to include the new rows and columns.
Format your table
- The next step is to customize the table design according to your preference. Whatever design you pick, ensure that the data is readable and different fields are easily distinguished.
- You can go with one of the default options provided by Excel, or select the colors yourself. A popular option is to alternate light and dark bands of colors for the rows so that each cell is distinctly readable, which prevents errors and confusion.
- If you aim to present the data on a large screen, avoid lighter colors and designs that are hard to read from a distance.
- Also give your table a name on the far left of the Design bar for easy identification.
Save your work!
- Before you go ahead and start trying out the various functions of Excel on your table, remember to save your spreadsheet.
- Don’t take the risk of having to start from scratch, and save your work every time you enter new data into your table. To do this go to File > Save As > enter the name of your database > Save button
Using formulas and functions in Excel for data analysis and manipulation
- Now that your basic database is all set, it’s time to explore the different functions Excel offers and gain insights from the data using the variety of tools available.
- Excel has numerous predefined formulae, like Average, Count, Sum, Maximum, Minimum, etc.
- Select the cell at the bottom of the column you want to use, and an arrow will appear with a dropdown of the different formulas you can use.
- Choose the formula you want, and it will automatically calculate and display the result in the selected cell. For example, if you select the column “Units sold” and perform the average function, Excel will display the average units sold based on the data in that column.
- Similarly, you can find out the total units sold, the maximum number of units sold, and so on.
- These simple calculations will give you great insights into your business operations, and aid in your decision making as a business owner.
- Of course, you can go beyond the basics and learn more about other features, formulae, and database functions. such as translating Excel files, to leverage Excel better.
Sorting and filtering data in Excel
- Sorting and filtering options: You can reorder the data however you like, by color, ascending order, or any custom filters.
- Quick totals: Quickly add up the data in your table using the Total row option present on the Design tab.
- Create dynamic charts: Present your table data in the form of charts using the Insert > Recommended Charts option to choose the chart you want. As you modify the table data, the charts you create will update automatically, which is extremely convenient and time saving.
- Calculated columns: Excel calculates an entire column for you just by entering a formula in the cell on the end of a single row. Once you press Enter the same formula is applied to all the other rows and adjusted accordingly.
- Structured references: You can create easy to understand formulas of your own as the structured references feature of Excel automatically uses the column headers instead of the cell addresses.
Get on top of data management for your business in a cost effective and convenient way using Excel’s Table functions. It’s a great tool to work with when just starting out, and it doesn’t take too much time or effort to figure out how to get the insights and analyzes you need to take your business to the next level.
Go beyond Excel: Work with database like Stackby
With excel dominating number crunching over the years, tools like Stackby gives you more than just a spreadsheet. Stackby helps you organize your data in 25+ unique column types, structure them more effectively, visualize them in different views other than a table, integrate them into your end-to-end workflows and collaborate with your team in real-time, from anywhere.
Google Sheets Vs Excel: Which is better for you? [2023]
If you work with excel or google sheet databases, you can easily import them in Stackby tables and continue to manage your data there. As a free tool, Stackby doesn’t require you to pay for additional licenses on our free forever plan as you need with Excel. Only when you hit the limits of the free plan, you can consider a subscription based on the number of seats you need.
Let Stackby take over your data management needs and ensure smoother operations & automated workflows for your teams. It enables you to create your own database, so you can truly excel in your business.
Free excel database templates & examples
Check out these free excel database templates to jumpstart your work.
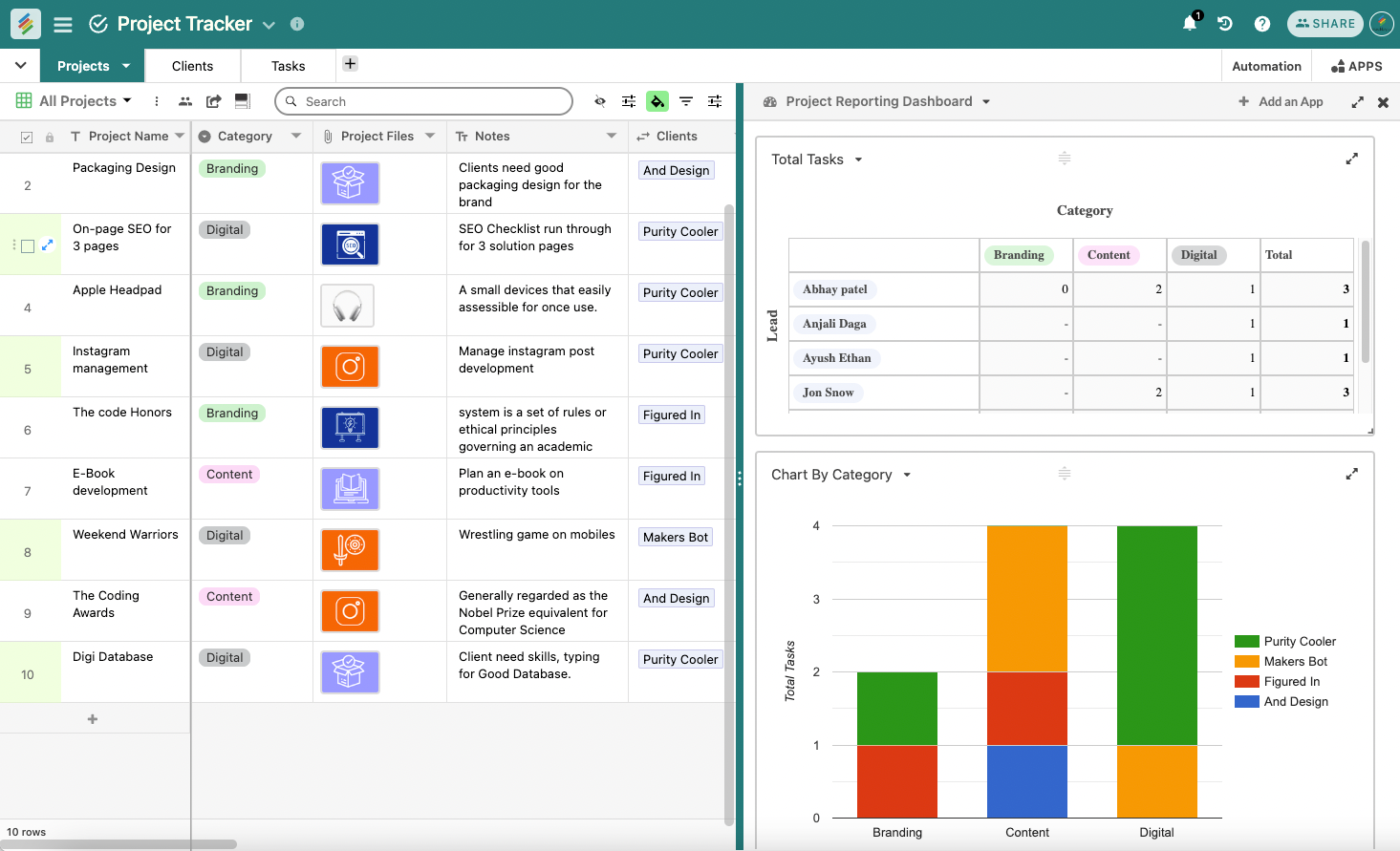
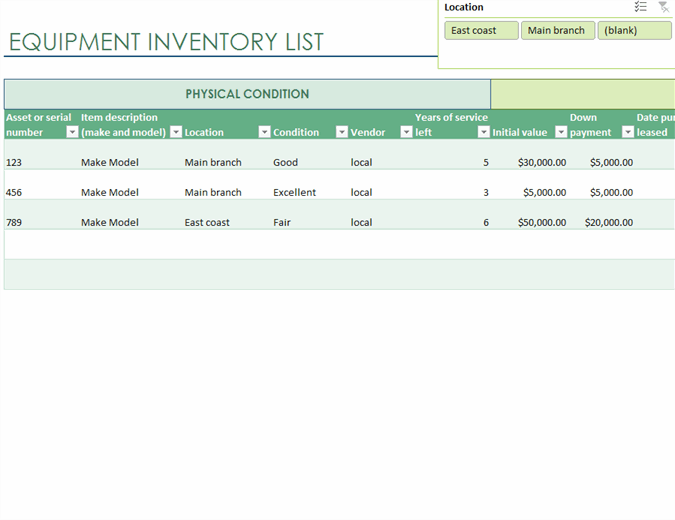
2. Excel's Equipment Inventory List Template
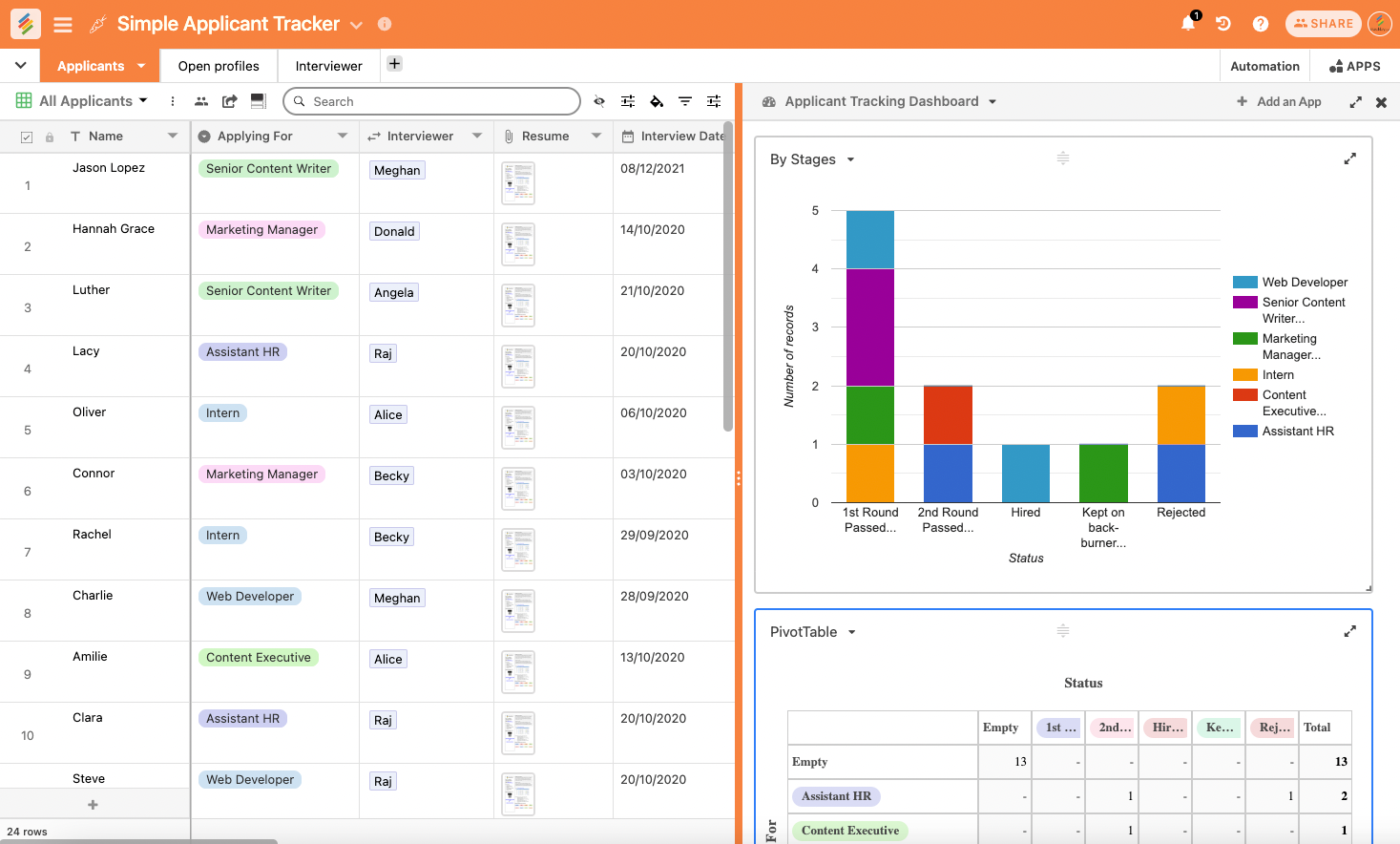
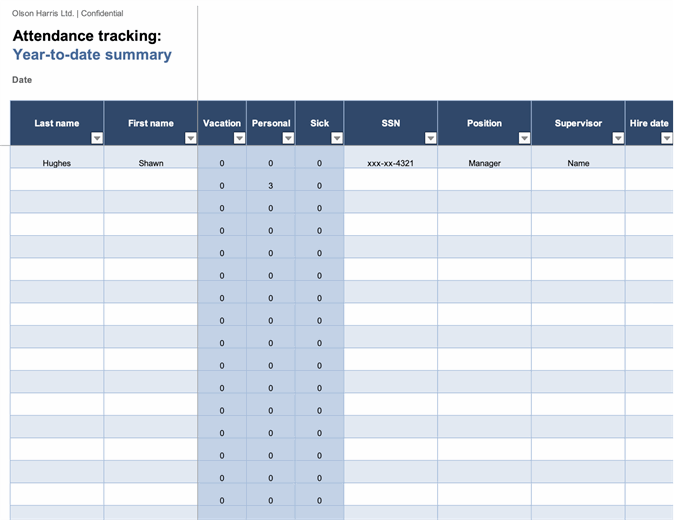
3. Excel's Employee Attendance Tracker Template
4. Content Production Template by Stackby


![A Simple Guide on Workflow Management Software [Updated 2024]](/blog/content/images/size/w960/2021/12/work-management-blog.png)



